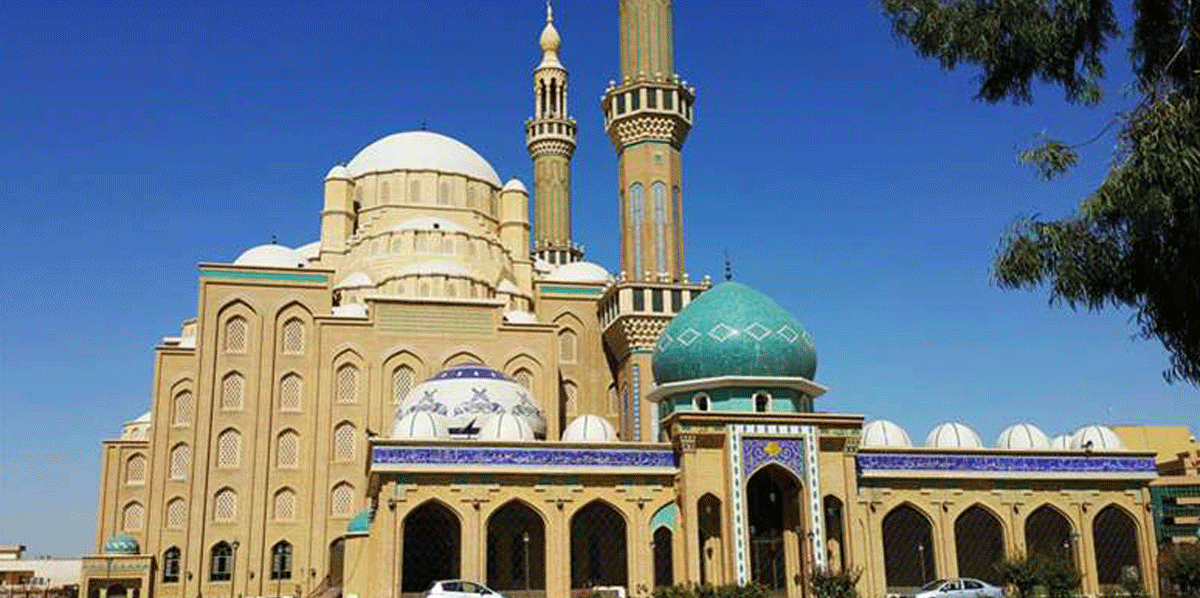
Kurdistan - Iraq
The Kurdistan Region is an autonomous region in northern Iraq comprising the four Kurdish-majority governorates of Dohuk, Erbil, Halabja and Sulaymaniyah and bordering Iran, Syria and Turkey.
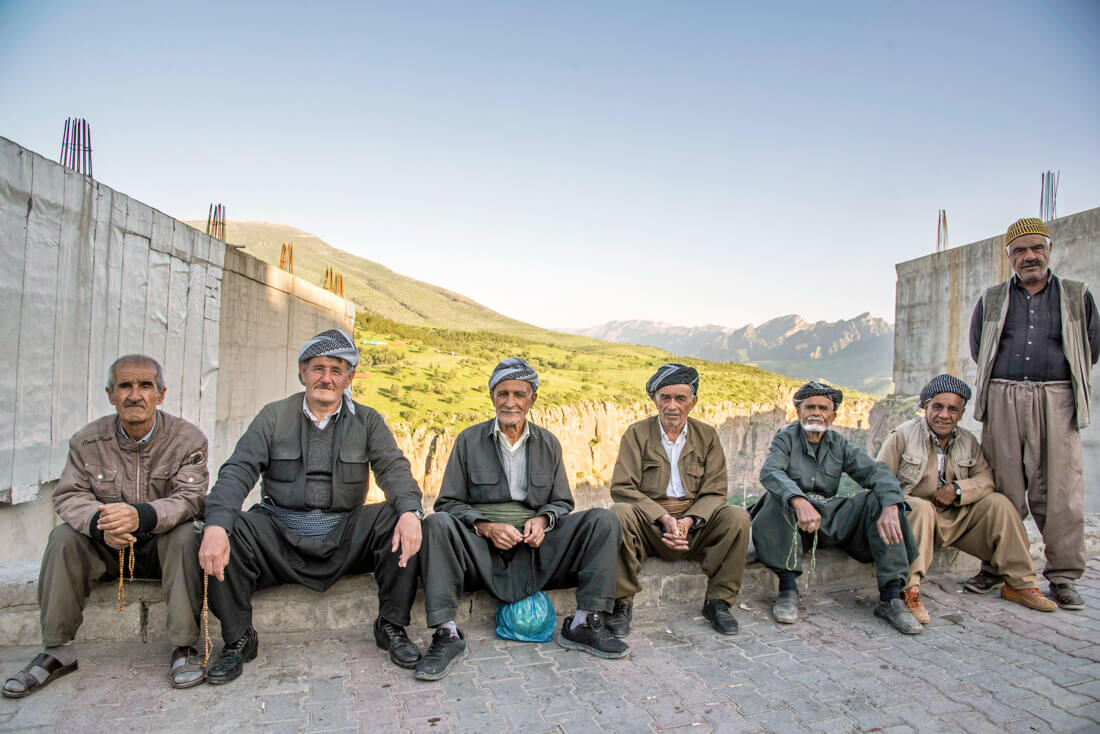

Kurdistan
People
The Kurdistan Region has a population of more than 5 million. In these past years the population has gone up to almost 7 million due to violence in Iraq and Syria causing displacement of people from the rest of Iraq, and from Syria. The region currently shelters nearly 250,000 refugees and 1.5 million internally displaced Iraqis.
Most Kurds speak at least two different languages fluently. They speak the language of their respective nationality and their mother tongue Kurdish. Greater Kurdistan also has several different dialects.
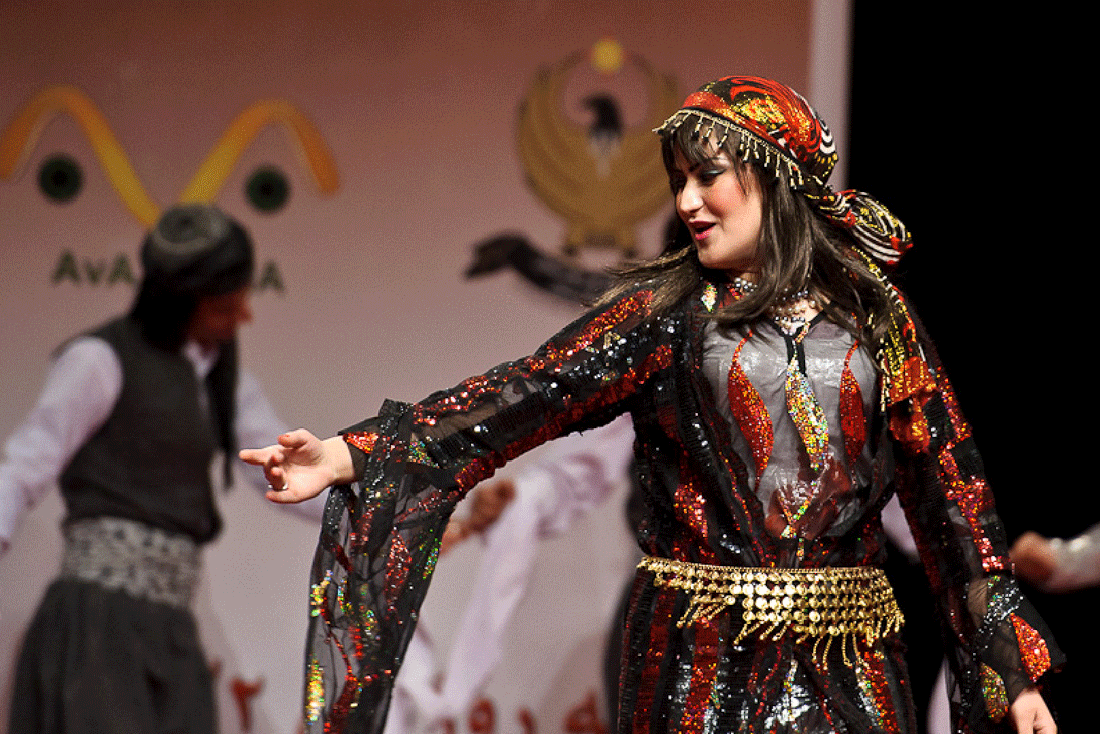

Kurdistan
Culture
Kurdish heritage is rooted in one of the world's oldest cultures. The earliest known evidence of a unified and distinct culture (and, possibly, ethnicity) of the inhabitants of the Kurdish mountains dates back to the Halaf culture of 5400 - 6000 B.C. This was followed which was a foreign introduction from Mesopotamia. Kurds consider themselves Indo-European descendants of the Guti, Hattians, Kassites, Mitanni, Mannai, Urartu, and Mushku groups. All of these peoples shared a common identity and spoke one language or closely related languages or dialects. According to the Encyclopedia Kurdistanica, Kurds are the descendants of all those who settled in Kurdistan historically, not of any one particular group. Those ancestors include the Guti (Kurti), Mede, Mard, Carduchi (Gordyaei), Adiabene, Zila and Khaldi. This heritage has been subject to injustices, neglect and repression, or has been eclipsed by other cultures. Important components of the Kurds' original cultural heritage have disappeared or have been destroyed. There are numerous examples of how valuable or irreplaceable Kurdish physical heritage has been endangered or destroyed, such as the threat posed by the Illusi Dam in Turkey, where the ancient Kurdish city of Hasankeyf could soon be covered by water.
Kurdistan
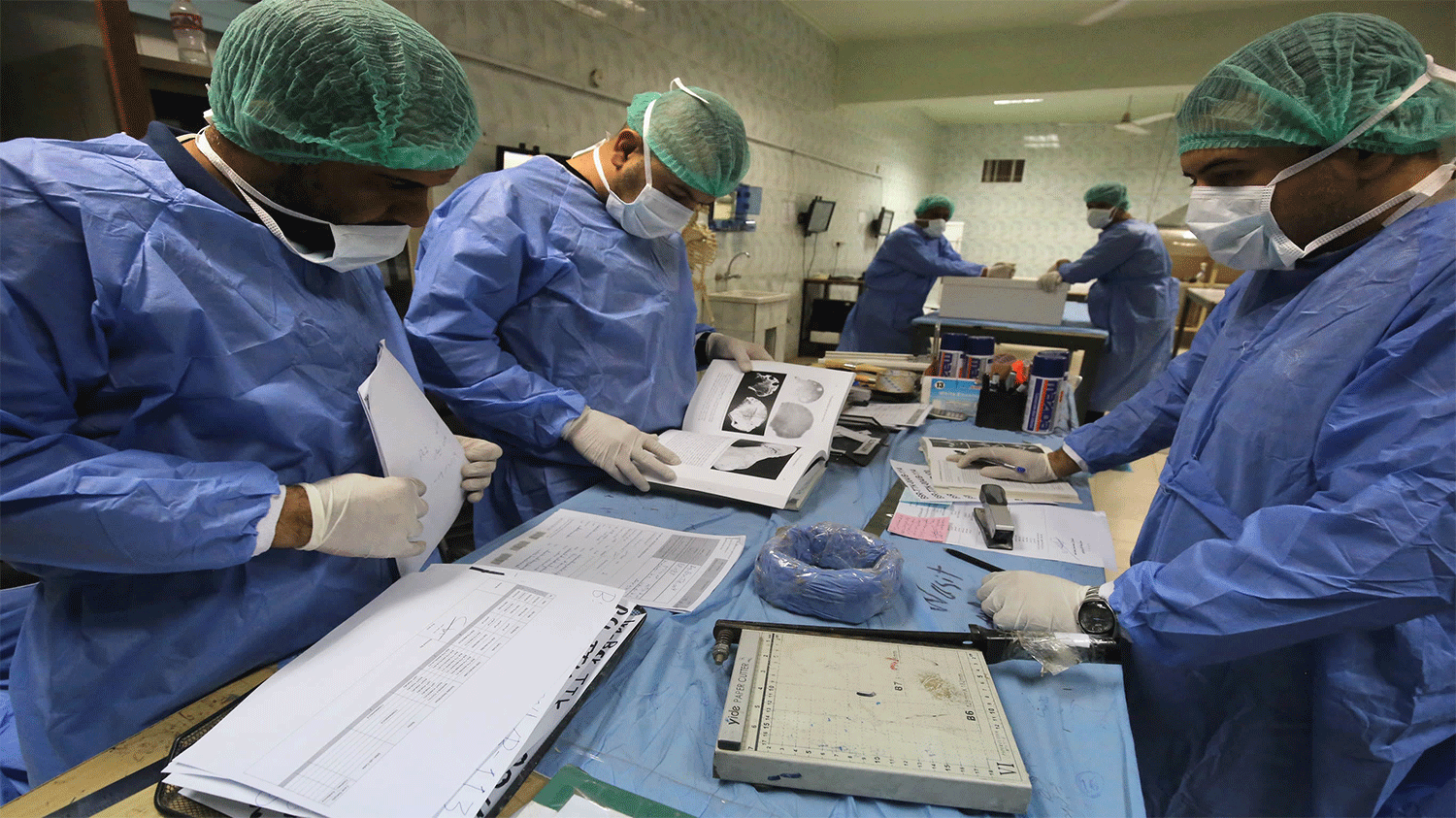
Healthcare
Health services are readily available in the Kurdistan Region of Iraq for free. Vast improvements in the health sector have been made in recent years.A good number of emergency hospitals have opened up and a drive has been underway to attract expat Iraqi physicians, with experience of western healthcare, to return to the region. During the Corono virus lockdown, FastCare- an initiative by telecom company FastLink provided mobile medical teams to visit families by calling specific numbers for each Kurdish governorate. There are both government funded and privately run hospitals in Erbil, Sulemani that cover a wide range of specialties. Some of the most notable include the Emergency Hospital (with trauma and burn center). The number for the ambulance service is 122.
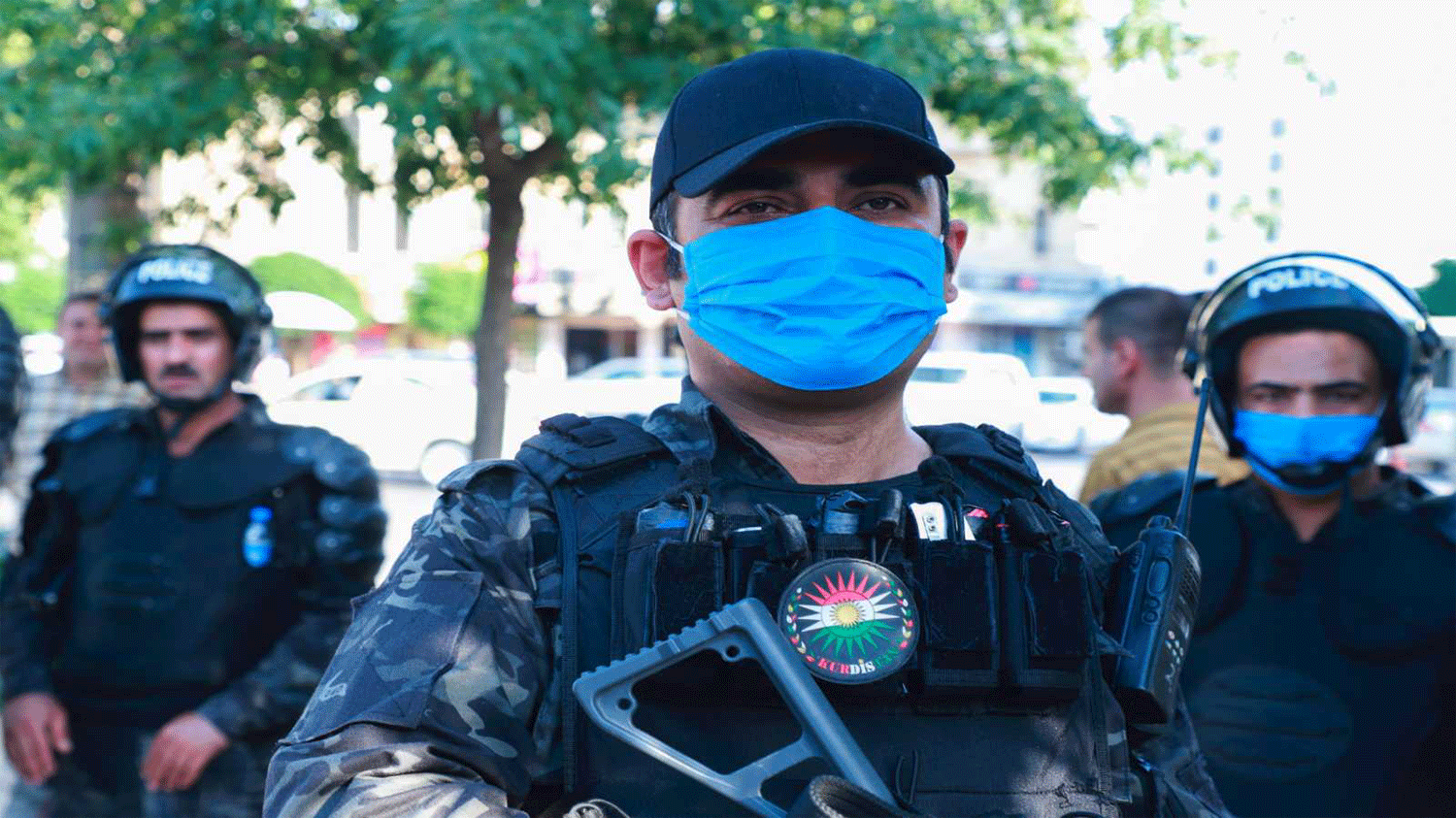

Kurdistan
Safety
Iraqi Kurdistan is a semi-autonomous region located in the north of the country. Technically, is the same country but Kurdistan enjoys a significant degree of political autonomy, it has its own army, and visa rules which for most countries passports stamped at airport entry for free. Despite being in a region surrounded by war and instability moreover, Kurdistan is one of the safest region and the most stable region of the country. There are many checkpoints in to the city which are extremely successful in deterring crime, and the strong presence of Peshmerga (the Kurdish military forces), also keeps the peaceful. The emergency number for the police is 144 or 24 or 104. These numbers can be dialed from mobile phones or landlines.